May 28, 2015 — OrbusNeich has announced that the first U.S. patient has been enrolled in the HARMONEE (Harmonized Assessment by Randomized, Multi-center Study of OrbusNEich's COMBO StEnt) stent study. The study is being conducted under the framework of the joint Japan-U.S. Harmonization-By-Doing (HBD) initiative and will support the company's planned application for Shonin approval in Japan and to meet the feasibility trial requirements in the U.S.
The study is a multi-center, single-blind, randomized, active-controlled, clinical trial in percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) subjects. Several additional sites are open and actively screening.
The HARMONEE study will enroll 572 patients at up to 50 study locations in Japan and the U.S. The first patient was enrolled at Shonan Kamakura General Hospital, Japan in February 2014. The study's endpoint is a comparison of clinically driven target vessel failure (TVF), defined as cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction (MI) or ischemia-driven target vessel revascularization (TVR) by percutaneous or surgical methods. All patients will undergo fractional flow reserve (FFR) or angiography to determine ischemia-driven TVR.
"The enrollment of the first U.S. patient marks a key milestone in the initiation of the U.S. Investigational Device Exemption portion of the HARMONEE study," said Roxana Mehran, M.D., director of interventional cardiovascular research and clinical trials, Mount Sinai Medical Center, and principal investigator in the U.S. "This randomized controlled trial is the first to use both physiologic and anatomic assessment of the long-term result of the stent procedure, as well as using high-resolution imaging of vascular healing, and it will provide important data that will inform the care of patients with coronary artery disease."
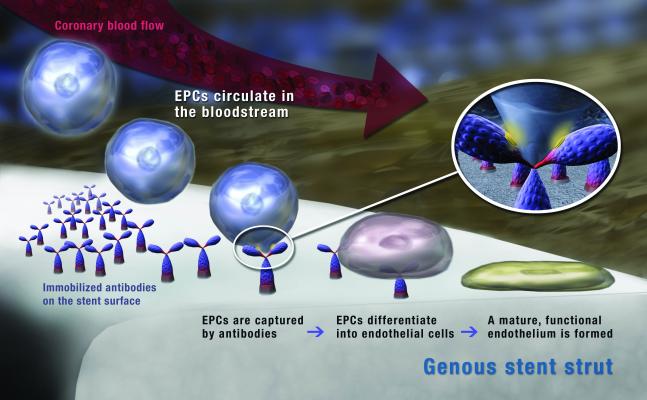
COMBO is a dual therapy stent designed to repair vessel injury and regenerate endothelium, fostering natural, true vessel healing. It does this by accelerating endothelial coverage and controlling neo-intimal proliferation. This is done through a combination of the EPC (endothelial progenitor cell) capturing technology and a sirolimus drug elution, delivered from a bioresorbable polymer that is completely degraded within 90 days.
OrbusNeich's patented endothelial progenitor cell (EPC) capture technology promotes the accelerated natural healing of the vessel wall after the implantation of blood-contact devices such as stents. The technology consists of an antibody surface coating that captures EPCs circulating in the blood to the device to form an endothelial layer that provides protection against thrombosis and modulates restenosis.
For more information: www.orbusneich.com


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









