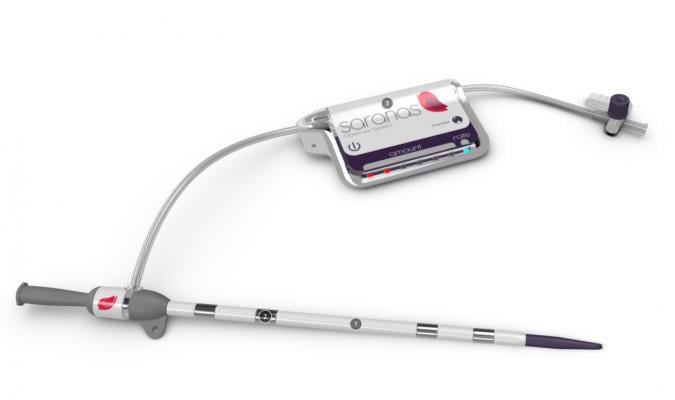
June 18, 2019 – New study results validate the effectiveness of the Saranas Early Bird Bleed Monitoring System to sense bleeding events during endovascular-related procedures by using sensors to detect relative changes in tissue bioimpedance. The study enrolled 60 patients from five sites who underwent an endovascular procedure and detected bleeding in more than half of patients. The results of this study were presented as late- breaking clinical research on at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography Interventions (SCAI) 2019 Scientific Sessions, May 19-22 in Las Vegas.
One in five patients experience a bleeding complication during large-bore endovascular procedures such as transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), endovascular aneurysm repair and percutaneous left ventricular assist device implant. This complication is associated with significant increase in risk of mortality, length of hospital stay and healthcare costs, according to a 2017Journal of the American Medical Association study. The Early Bird is designed to be integrated during endovascular procedures and inserted in a vessel in anticipation of a bleed. The technology was invented at the Texas Heart Institute in Houston.
From August 2018 to December 2018, a total of 60 patients (mean age 76 years, 42 percent females) from five U.S. sites were enrolled and underwent an endovascular procedure (TAVR) 67 percent; percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) 13 percent; Impella 8 percent; balloon aortic valvuloplasty 7 percent; transcatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR) 2 percent, endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) 2 percent and MitraClip 2 percent). The Early Bird was used during and after endovascular procedures, either as a venous or arterial access sheath. In the case of bleeding, the device has a sensor that detects the onset of bleeding and characterizes bleed progression into I, II and III levels. The primary endpoint was the level of agreement in bleeding detection between the Saranas Early Bird and post-procedural computed tomography (CT).
Early Bird detected bleeding in 63 percent of patients, with 33 percent of those patients at bleeding level I, 23 percent at bleeding level II and seven percent at bleeding level III. No device-related complications were reported.
“This is the first time we’re seeing how this device could help in a real-world patient setting and we were very encouraged by the results. Right now, patients have a risk of vessel injury when undergoing endovascular procedures where the femoral artery or vein is used for vascular access,” said Philippe Genereux, M.D., principal investigator, cardiologist and physician at Morristown Medical Center in Morristown, N.J. “This technology allows us to detect bleeding in real time, which means we can take action quickly and improve the outcomes of the procedure and recovery for the patient.”
In March, the Early Bird device was granted de novo classification by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Saranas plans to conduct a controlled rollout to institutions interested in having bleed management as part of their standard of care.
The authors note plans to continue research of the device with controlled studies at institutions who have specific interest in bleed management. Post-approval study and practices will evolve as the authors continue to evaluate and collect data on the device.
For more information: www.saranas.com


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









