Using new high-resolution microscopy, researchers have found that molecular struts called microtubules (MT) interact with the heart’s contractile machinery to provide mechanical resistance for the beating of the heart.
Konica Minolta introduced the latest version of the Sonimage HS1 compact ultrasound system, enabling improved image quality, streamlined workflow and new cardiac functionality for the point-of-care ultrasound market.
Boston Scientific has received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for a suite of products deemed safe for use in a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) environment.
Cardiac PET/CT represents a major advancement in cardiovascular diagnostics, offering significant clinical and ...
April 28, 2016 — Breast cancer patients undergoing treatment with trastuzumab-containing regimens should be monitored ...

April 28, 2016 — Abbott and St. Jude Medical Inc. announced a definitive agreement for Abbott to acquire St. Jude ...
The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) issued a proposal to align and modernize how Medicare payments are tied to the cost and quality of patient care for hundreds of thousands of doctors and other clinicians.
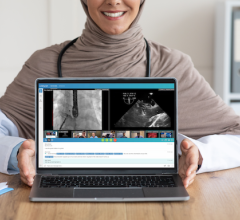
SPONSORED CONTENT — Studycast is a comprehensive imaging workflow system that allows healthcare professionals to work ...
April 27, 2016 — Imaging Advantage LLC, platform provider of cloud-based radiology service, announced the launch of a ...
Veniti Inc. announced the first successful treatment with the Vici Verto Venous Stent System of a patient suffering from post-thrombotic syndrome (PTS) associated with venous outflow obstruction.
Mitralign Inc. announced its Mitralign Percutaneous Annuloplasty System (MPAS) has received CE mark approval from its notified body, the British Standards Institution (BSI), for the treatment of functional mitral regurgitation (FMR).
Providing exceptional cardiovascular care for patients to achieve the best possible outcomes is the number one goal for ...
The results of a secondary analysis of the SCOT-HEART trial show that coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) leads to a more appropriate and effective selection of invasive coronary angiography for patients with suspected angina due to coronary heart disease.
Taking long naps or being excessively tired during the day is associated with a higher risk for developing metabolic syndrome, according to a study presented at the American College of Cardiology’s 65th Annual Scientific Session.
Auris Surgical Robotics Inc. and Hansen Medical Inc. announced that they have signed a definitive merger agreement under which Auris will acquire Hansen Medical for $4.00 per share in cash.
Cardiac positron emission tomography (PET) is growing in popularity among cardiologists because it provides the ability ...
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) announced that it has created a Web-based guidance tool for developers of health-related mobile applications (health apps).
The American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT) has launched Vascular Interventional Essentials, a new educational program that explores the image-guided procedures of interventional radiology.
Scientists have found that a greater number of patients with coronary artery disease may benefit from coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery than previously thought.


 April 29, 2016
April 29, 2016