September 8, 2014 — The U.S, Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared MicroVention Inc.’s Low-Profile Visualized Intraluminal Support Device (LVIS and LVIS Jr.), which is a stent and delivery system used to treat certain brain aneurysms.
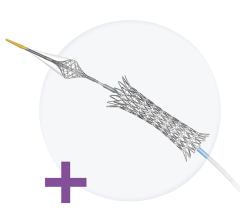
The stent is a self-expanding, nickel-titanium (nitinol) single wire braid. The delivery system consists of an introducer and delivery wire and is used to deliver the stent to the aneurysm. The stent keeps the soft platinum coils that are put into the aneurysm from slipping back into the main blood vessel.
The LVIS Device is intended for use with soft platinum coils for the treatment of unruptured, wide-neck brain (intracranial, saccular) aneurysms. The stent serves two functions. One, it supports the coils so they block the aneurysm and two, the stent prevents the coils from slipping back into the main blood vessel.
How it works:
- Using a guidewire, a small catheter (microcatheter) is advanced into the blood vessel along the aneurysm.
- The guidewire is removed and the microcatheter remains in place allowing for the proper insertion of the LVIS device.
- The physician positions the device to be released (deployed) and carefully retracts the microcatheter. The physician then advances the delivery wire allowing the LVIS device to be deployed across the neck of the aneurysm.
- The stent expands as it exits the microcatheter.
- After the microcatheter is positioned in the aneurysm, soft platinum coils are delivered into the aneurysm to block the flow of blood into the aneurysm.
- The LVIS device serves as a support for the coils to prevent them from moving back into the blood vessel.
The LVIS Device should not be used in:
- Patients who cannot take medications that thin the blood and prevent blood clots.
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to metal, such as nickel-titanium and metal jewelry. Patients with anatomy that does not allow passage or deployment of the LVIS device.
- Patients with an active bacterial infection.
- Patients with a pre-existing stent in place at the target aneurysm.
For more information: www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf13/H130005a.pdf


 November 24, 2025
November 24, 2025