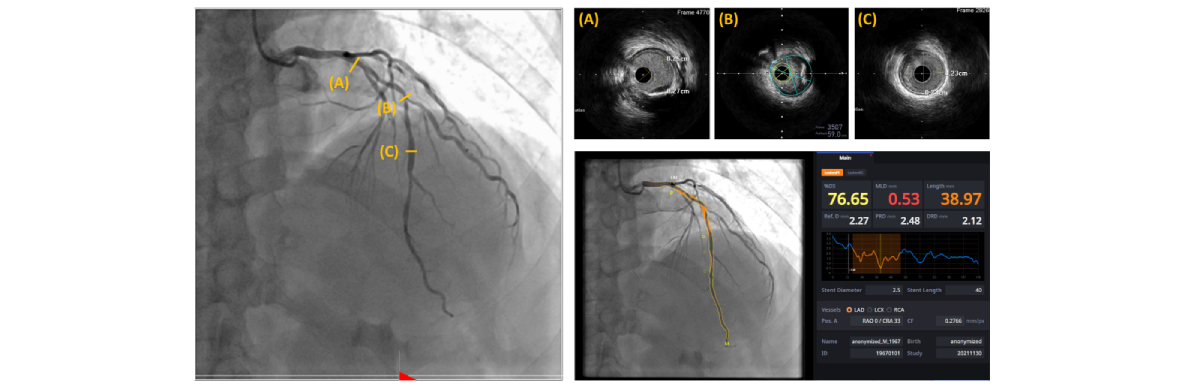
A representative case in which artificial intelligence–based quantitative coronary angiography (AI-QCA) showed a good correlation with intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) observation. %DS: percent diameter stenosis; DRD: distal reference diameter; LAD: left anterior descending artery; LCX: left circumflex artery; MLD: minimal luminal diameter; PRD: proximal reference diameter; RCA: right coronary artery; Ref.D: reference diameter.
June 12, 2023 — New research published in JMIR Cardio reveals the remarkable potential of artificial intelligence (AI) technology in analyzing coronary angiography, a common diagnostic procedure for coronary artery disease. Led by Dr In Tae Moon, the study conducted at Uijeongbu Eulji University Hospital in Korea showcases the power of AI-based quantitative coronary angiography (AI-QCA) in enhancing clinical decision-making.
The study compared AI-QCA to intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), to validate its performance. IVUS is a widely used imaging tool to assess coronary artery stenotic lesions. Simply put, these lesions can cause narrowing of the coronary arteries and restrict blood flow to the heart. The analysis included 54 significant lesions from 47 patients who underwent IVUS-guided coronary intervention. The researchers found that AI-QCA provided accurate and consistent measurements of coronary stenotic lesions, similar to IVUS, thus suggesting it could be safely used in clinical practice.
The AI-QCA analysis was performed using MPXA-2000 (Medipixel), a newly developed software which uses an algorithm intended to mimic the QCA process by human experts. AI-enabled QCA can automatically analyze 2D angiography images and thus guide physicians in determining optimal stent sizes. This technology thus has potential to improve patient outcomes and support clinical decision-making. “We believe that this novel tool could provide confidence to treating physicians and help in making optimal clinical decisions,” emphasized Dr Moon, the lead author of the study.
AI-QCA offers an innovative approach to analyze coronary angiography images, providing automated and real-time insights. This study marks an important step forward in the application of AI to improving cardiovascular care. While the study provides promising results, further research is required to fully explore the clinical utility and safety of AI-QCA.
For more information, read the full article titled “Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence–Based Automated Quantitative Coronary Angiography Compared to Intravascular Ultrasound: Retrospective Cohort Study” published in the open access journal JMIR Cardio.
For more information: https://cardio.jmir.org/


 October 24, 2025
October 24, 2025