November 8, 2017 — Investigators in the FAVOR II China and FAVOR II Europe-Japan studies recently presented their results at the 2017 Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) annual conference, Oct. 29-Nov. 2, in Denver.
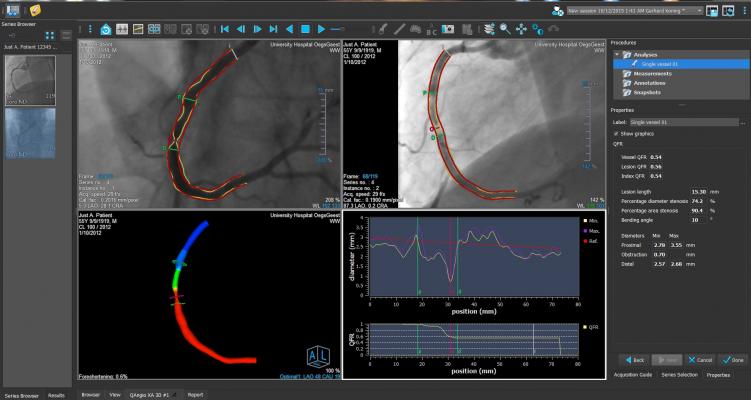
The FAVOR II China trial evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of quantitative flow ratio (QFR), a novel angiography-based method for deriving fractional flow reserve (FFR) without pressure wire or induction of hyperemia, in diagnosing hemodynamically-significant coronary stenosis as defined by FFR. Between June and July 2017, 308 patients were enrolled. Patient-level and vessel-level diagnostic accuracy of QFR were 92.4 percent (95 percent CI: 88.9-95.1 percent) and 92.7 percent (95 percent CI: 89.3-95.3 percent), both significantly higher than the prespecified target value (P<0.001). Sensitivity and specificity in identifying hemodynamically-significant stenosis were significantly higher for QFR than QCA.
“FAVOR II China showed that QFR has high feasibility and accuracy in identifying hemodynamically-significant coronary stenosis,” said Bo Xu, MBBS, director, catheterization laboratories at Fu Wai Hospital in Beijing, China. "It also demonstrates the clinical utility of QFR for use in diagnostic catheterization laboratories. QFR has the potential to improve angiography-based identification of functionally-significant stenosis during coronary angiography.”
FAVOR II Europe-Japan was a prospective observational, investigator-initiated study performed at 11 hospitals in Europe and Japan from March 2017 to October 2017 with a primary endpoint of sensitivity and specificity of QFR compared to two-dimensional QCA (2D-QCA) with FFR as reference standard. The study found that QFR had higher sensitivity (88 percent vs. 46 percent, P<0.001) and specificity (88 percent vs. 77 percent, P<0.001) compared to 2D-QCA. Key secondary endpoints of feasibility of QFR (defined as the fraction of vessels with successful FFR measurements where in-procedure QFR is computed) was 97 percent (N=373) and time to QFR was 4.8 minutes (IQR: 3.5-6.0) compared to 7 minutes for FFR (IQR: 5.0-10.0), P<0.001.
“QFR showed superior sensitivity and specificity for detection of functional significant lesions in comparison with 2D-QCA using FFR as reference standard,” said Jelmer Westra, MS, research fellow at Aarhus University Hospital in Aarhus N, Denmark. “In addition, in-procedure QFR computation was feasible and was computed within the time of standard FFR measurements. Still, randomized trials are needed to determine if a QFR-based diagnostic strategy provides non-inferior clinical outcomes compared to pressure wire based strategies.”
The FAVOR II Europe Japan study was funded by Aarhus University Hospital, Skejby and participating institutions. The QFR solution was provided for free during the study period. The FAVOR II CHINA trial was funded by Pulse medical imaging technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, and the Natural Science Foundation of China.
For more information: www.tctconference.com
Related Content
TCT 2017 Late-breaking Clinical Trial Presentations
Reference:


 October 24, 2025
October 24, 2025