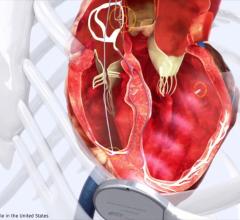
April 18, 2016 — St. Jude Medical Inc. announced the U.S. launch and first U.S. implants of the Quadra Assura MP cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator (CRT-D) with MultiPoint Pacing Technology. Previously approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), MultiPoint Pacing technology is a new approach designed for CRT patients who are not responsive to other pacing options.
The first implant took place at Saint Francis Hospital in Hartford, Conn. Speaking about the opportunity, Neal Lippman, M.D., electrophysiologist with Arrhythmia Consultants of Connecticut at Saint Francis said, “We are now able to offer St. Jude Medical’s new MultiPoint Pacing technology for our patients whose heart failure condition is difficult to manage. It is important for us to have this option to individualize patient care and help improve response to therapy.”
Despite the improvements in patient outcomes seen with quadripolar CRT technology, a small but important group of patients do not respond optimally to the therapy. Importantly, these non-responders to CRT cannot be identified at the time of implant, and how effective the therapy will be in addressing an individual patient’s heart failure symptoms can be unpredictable. MultiPoint Pacing technology offers physicians a new set of tools that allow for individualized patient therapy with the goal of optimizing their response to CRT.
Cardiac resynchronization therapy includes a lead (Quartet Quadripolar LV Lead) placed on the lower left chamber of the heart (ventricle). The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood from the heart out to the rest of the body. MultiPoint Pacing technology is designed to deliver electrical pulses to multiple locations on the Quartet lead to make the heart’s lower chambers pump in a more coordinated way to mirror the natural contractions of a healthy heart.
According to the American Heart Association, CRT can improve the heart’s efficiency at pumping blood to the body and can lessen symptoms of heart failure, including shortness of breath. However, even with effective placement of the leads around the heart, therapy can be unpredictable and ineffective for some patients. MultiPoint Pacing technology allows physicians to program the device to stimulate more left-ventricular tissue at one time by pacing at multiple locations in the heart, more similar to the natural electrical behavior of the heart. Over 60 abstracts and publications demonstrate that this increases the number of patients who benefit from this type of therapy (CRT).
A recent study demonstrated that the St. Jude Medical MultiPoint Pacing technology may be particularly beneficial in patients not responding to traditional bi-ventricular pacing therapy, which accounts for approximately one-third of the total population of patients receiving CRT. In this study, MultiPoint Pacing technology realized a 90 percent responder rate for patients with the technology at one year compared to traditional methods of CRT. Several ongoing studies continue to build the body of evidence and examine the benefits patients receive, including the St. Jude Medical MORE CRT MPP clinical study.
Data from the MultiPoint Pacing Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) study will be presented during a late-breaking clinical trial session during the Heart Rhythm Society’s (HRS) 37th annual scientific sessions, May 4 – 7 in San Francisco.
Approximately 23 million people worldwide are afflicted with congestive heart failure and 2 million new cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Studies have shown that CRT can improve the quality of life for many patients with heart failure, a progressive condition in which the heart weakens and loses its ability to pump an adequate supply of blood. The CRT technology resynchronizes the lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart by sending uniquely programmed electrical impulses to stimulate each ventricle to beat in sync for optimal cardiac performance.
For more information: www.sjm.com


 July 21, 2025
July 21, 2025