May 21, 2024 — A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 8, entitled, “Associations among NMR-measured inflammatory and metabolic biomarkers and accelerated aging in cardiac catheterization patients.”
Research into aging has grown substantially with the creation of molecular biomarkers of biological age that can be used to determine age acceleration. Concurrently, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) assessment of biomarkers of inflammation and metabolism provides researchers with new ways to examine intermediate risk factors for chronic disease.
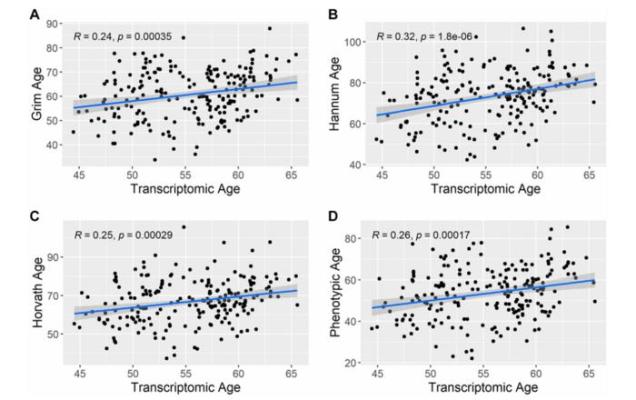
In this new study, researchers Henry Raab, Elizabeth R. Hauser, Lydia Coulter Kwee, Svati H. Shah, William E. Kraus, and Cavin K. Ward-Caviness from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and Duke University used data from a cardiac catheterization cohort to examine associations between biomarkers of cardiometabolic health and accelerated aging assessed using both gene expression (Transcriptomic Age) and DNA methylation (Hannum Age, GrimAge, Horvath Age, and Phenotypic Age).
“This study utilizes the CATHGEN cohort from the Jiang et al. study to investigate associations between multiple epigenetic and transcriptomic aging biomarkers and a broad array of NMR-based measures of inflammation, lipid homeostasis, and diabetes risk.”
Linear regression models were used to associate accelerated aging with each outcome (cardiometabolic health biomarkers) while adjusting for chronological age, sex, race, and neighborhood socioeconomic status. Their study shows a robust association between GlycA and GrimAge (5.71, 95% CI = 4.36, 7.05, P = 7.94 × 10−16), Hannum Age (1.81, 95% CI = 0.65, 2.98, P = 2.30 × 10−3), and Phenotypic Age (2.88, 95% CI = 1.91, 3.87, P = 1.21 × 10−8). The researchers also saw inverse associations between apolipoprotein A-1 and aging biomarkers.
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205758


 February 03, 2026
February 03, 2026 









