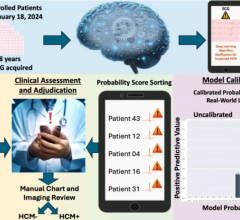
An example of a body composition analysis of an abdominal CT slice with the subcutaneous fat in green, skeletal muscle red and visceral fat in yellow. This was automatically identified and analyzed via a deep learning algorithm to assess the risk for heart attack and stroke in more than 12,000 patients.
December 2, 2020 – Automated deep learning analysis of abdominal computed tomography (CT) images produces a more precise measurement of body composition and predicts major cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke, better than overall weight or body mass index (BMI), according to a study presented today at the 2020 Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) virtual meeting.
“Established cardiovascular risk models rely on factors like weight and BMI that are crude surrogates of body composition,” said Kirti Magudia, M.D., Ph.D., an abdominal imaging and ultrasound fellow at the University of California San Francisco. “It’s well established that people with the same BMI can have markedly different proportions of muscle and fat. These differences are important for a variety of health outcomes.”
Unlike BMI, which is based on height and weight, a single axial CT slice of the abdomen visualizes the volume of subcutaneous fat area, visceral fat area and skeletal muscle area. However, manually measuring these individual areas is time intensive and costly.
As a radiology resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Magudia was part of a multidisciplinary team of researchers, including radiologists, a data scientist and biostatistician, who developed a fully automated method using deep learning — a type of artificial intelligence (AI) — to determine body composition metrics from abdominal CT images.
“Abdominal CT scans that are routinely performed provide a more granular way of looking at body composition, but we’re not currently taking advantage of it,” Magudia said.
The study cohort was derived from the 33,182 abdominal CT outpatient exams performed on 23,136 patients at Partners Healthcare in Boston in 2012. The researchers identified 12,128 patients who were free of major cardiovascular and cancer diagnoses at the time of imaging. Mean age of the patients was 52 years, and 57% of patients were women.
The researchers selected the L3 CT slice (from the third lumbar spine vertebra) and calculated body composition areas for each patient. Patients were then divided into four quartiles based on the normalized values of subcutaneous fat area, visceral fat area and skeletal muscle area.
In this retrospective study, it was determined which of these 12,128 patients had a myocardial infarction (heart attack) or stroke within five years after their index abdominal CT scan. The researchers found 1,560 myocardial infarctions and 938 strokes occurred in this study group.
Statistical analysis demonstrated that visceral fat area was independently associated with future heart attack and stroke. BMI was not associated with heart attack or stroke.
“The group of patients with the highest proportion of visceral fat area were more likely to have a heart attack, even when adjusted for known cardiovascular risk factors,” Magudia said. “The group of patients with the lowest amount of visceral fat area were protected against stroke in the years following the abdominal CT exam.”

“These results demonstrate that precise measures of body muscle and fat compartments achieved through CT outperform traditional biomarkers for predicting risk for cardiovascular outcomes,” she added.
According to Magudia, this work demonstrates that fully automated and normalized body composition analysis could now be applied to large-scale research projects.
“This work shows the promise of AI systems to add value to clinical care by extracting new information from existing imaging data,” Magudia said. “The deployment of AI systems would allow radiologists, cardiologists and primary care doctors to provide better care to patients at minimal incremental cost to the health care system.”
This paper is the recipient of an RSNA 2020 Trainee Research Prize.
Co-authors are Christopher P. Bridge, D.Phil., Camden P. Bay, Ph.D., Florian J. Fintelmann, M.D., Ana Babic, Ph.D., Katherine P. Andriole, Ph.D., Brian M. Wolpin, M.D., and Michael H. Rosenthal, M.D., Ph.D.
Watch the RSNA presentation of this study in the VIDEO: Deep Learning Analysis of Abdominal Fat to Assess Heart Attack and Stroke Risk.



 September 24, 2025
September 24, 2025