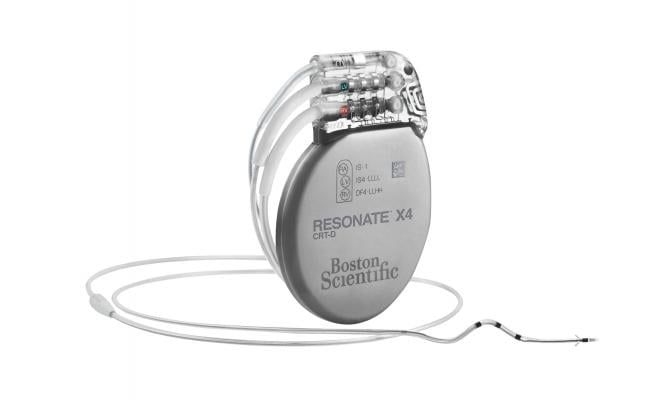
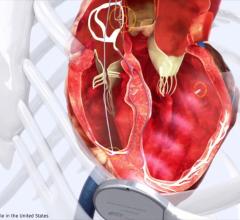
October 20, 2017 — Boston Scientific announced new data from the Multisensor Chronic Evaluation in Ambulatory Heart Failure Patients (MultiSENSE) study evaluating the performance of the HeartLogic Heart Failure Diagnostic to predict impending heart failure (HF) decompensation. Data from the study were presented as a late-breaking clinical trial at the Heart Failure Society of America's 21st Annual Scientific Meeting, Sept. 16-19 in Dallas, and confirmed the HeartLogic Diagnostic accurately enhanced the ability to classify patients at high or low-risk of experiencing a future HF event.
The HeartLogic Diagnostic provides continuous measurement of a patient's heart failure by combining data from sensors evaluating heart sounds, respiration rate and volume, thoracic impedance, heart rate and activity. Current clinical guidelines recommend the use of a blood test to measure natriuretic peptides BNP or NT-proBNP in order to diagnose HF or determine disease severity.1,2 However, the test can only reflect a snapshot assessment at the time of a blood draw, which loses relevance as a patient's condition changes.
New data from the MultiSENSE trial demonstrated the HeartLogic Diagnostic significantly expanded the ability of a baseline blood test to identify when patients were at an elevated risk of a HF event. The combination of the HeartLogic Diagnostic with a baseline NT-proBNP measurement accurately identified when patients within varying risk groups were at a 23 to 50 times increased risk of experiencing a HF event.
"Through the utilization of the HeartLogic Diagnostic, physicians can more accurately triage appropriate care to this vulnerable patient population in a timely manner, particularly when using the alert in combination with an intermittent measure of NT-proBNP," said John P. Boehmer, M.D., principal investigator and director of the Heart Failure Program at Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center and professor of medicine, Penn State College of Medicine.
The study included 900 patients who had enhanced sensor data collection enabled in their cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator (CRT-D) systems and were followed for up to one year.
Previously published study data demonstrated that the HeartLogic Diagnostic had an observed sensitivity of 70 percent as well as the ability to provide weeks of advance notice and low burden for detecting indications of worsening HF.
The company received CE Mark and U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of the HeartLogic Diagnostic within the Resonate family of implantable cardioverter defibrillator and CRT-D systems earlier this year. The new line of devices will become commercially available later this year.
For more information: www.bostonscientific.com
References
1. Yancy CW, Jessup M, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. Circulation. 2017;136:e137–e161. DOI: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000509.
2. Ponikowski P, Voors AA, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal 2016;37:2129-2200.


 July 21, 2025
July 21, 2025