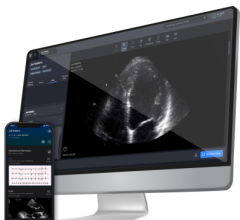
Representative still images of 4 of the 10 standard transthoracic echocardiographic views acquired by a nurse using the Caption Health deep-learning algorithm that were judged to be of diagnostic quality.
February 23, 2021 — A recent article in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Cardiology demonstrated that artificial intelligence software-guided cardiac ultrasound images captured by nurses without prior ultrasound experience and reviewed by experienced cardiologists were shown to be of diagnostic quality.[1] The study showed the quality was good enough to assess left ventricular size and function in 98.8% of patients, right ventricular size and function in 92.5% of patients, and in 98.8% of patients for presence of pericardial effusion.
The technology used was from artificial intelligence (AI) vendor Caption Health. The software offers AI guidance and interpretation for ultrasound. The Caption AI platform, which includes the Caption Guidance and Caption Interpretation, is the first AI-guided medical imaging acquisition software to obtain FDA clearance, enabling a broad range of healthcare workers to perform cardiac ultrasound examinations at the point of care.
“In our mission to democratize access to healthcare and quality medical imaging, we wanted to ensure that we tested Caption Guidance on a wide range of patients to prove its effectiveness across a diverse population,” said Yngvil Thomas, head of medical affairs and clinical development at Caption Health. “This study shows that AI-guided imaging can expand healthcare professionals’ skill sets in a meaningful way with minimal training — giving patients more opportunities to receive timely diagnostic care.”
Each patient in the study underwent paired ultrasounds: one from a nurse, and one from an experienced registered diagnostic cardiac sonographer. In addition to evaluating diagnostic quality, the cardiologists also made diagnostic assessments. For the diagnostic assessments corresponding to the primary endpoints listed above, there was at least 92.5% agreement between the nurse and sonographer scans. The results indicated that Caption Guidance performed well for patients with various cardiac pathologies that might be encountered in real-world clinical practice; more than 90% of patients were found to have cardiac abnormalities in scheduled full echocardiograms performed within two weeks of the study. The results were also consistent across BMI, sex, and race, further demonstrating Caption Guidance's efficacy and robustness.
“The study’s remarkable agreement between nurses’ scans and sonographers’ scans shows that the use of AI like Caption Guidance could fundamentally change how we use medical imaging,” said Akhil Narang, M.D., a cardiologist at Northwestern Medicine and first author on the paper. “This will extend the abilities of healthcare providers to evaluate for different pathologies in critical care, emergency departments and other settings — and perhaps identify them even earlier with the assistance of AI.”
The study was conducted with 240 patients aged 20-91, 42% female patients, with 17.6% of patients black, and 33% of patients with a BMI of 30 or greater.
Given the demonstrated effects of COVID-19 on the heart (Puntmann, Carerj, Wieters, et al in JAMA Cardiology),[2] the study notes that technology like Caption Guidance may allow for reduced exposure of sonographers to the disease. Caption AI has already been used in hospital systems for assessment and treatment of the cardiovascular impact of COVID-19, and is quickly becoming the new standard of care in critical care settings for timely diagnosis and management.
"Cardiac ultrasound is a powerful diagnostic technology that can be helpful, and even life-saving, in many clinical settings,” said Chris Moore, M.D., an emergency medicine physician at Yale. “However, its application may be limited by the availability of experienced users. This groundbreaking study represents a significant step forward in making this technology more widely accessible to patients wherever needed."
In addition to further refinements of its cardiac ultrasound guidance, Caption Health recently received a $4.95 million grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to develop AI-guided lung ultrasound software.
For more information: captionhealth.com
Related Caption Health AI-guided Echocardiogram Content:
Northwestern Medicine Introduces Artificial Intelligence to Improve Ultrasound Imaging
Innovative Cardiovascular Ultrasound Solutions Showcased at ASE 2020 Virtual Meeting
FDA Clears Caption Health AI-assisted Point-of-care Ejection Fraction Evaluation
FDA Clears Cardiac Ultrasound Software With Artificial Intelligence to Guide User
Reference:


 September 24, 2025
September 24, 2025