Less-invasive procedures to open severely clogged leg arteries were as good at helping people survive and avoid amputation as more invasive open surgeries, according to a new study. The results were reported in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, an American Heart Association journal.
Clinical trials are a critical tool for getting new treatments to people who need them, but research shows that difficulty finding the right volunteer subjects can undermine the effectiveness of these studies. Researchers at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center designed and tested a new computerized solution that used artificial intelligence (AI) to effectively identify eligible subjects from electronic health records (EHRs), allowing busy clinical staff to focus their limited time on evaluating the highest quality candidates.
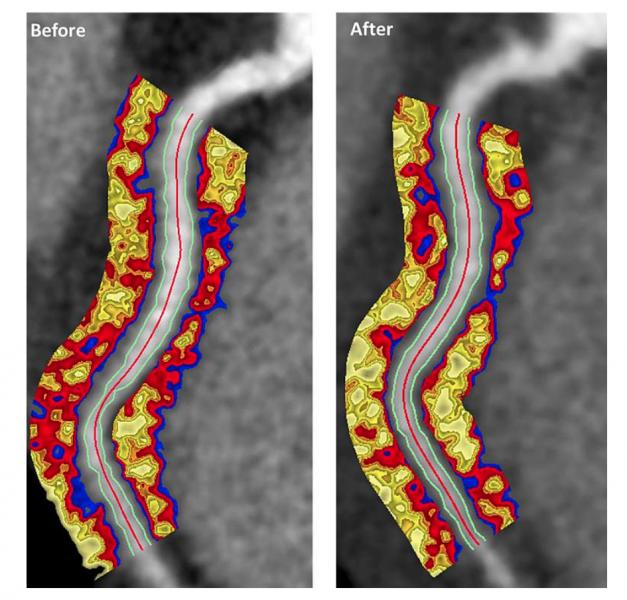
July 31, 2019 — Researchers found anti-inflammatory drug therapies used to treat moderate to severe psoriasis can ...
Providing exceptional cardiovascular care for patients to achieve the best possible outcomes is the number one goal for ...
The chances of patients experiencing complications after having a cardiac device implanted vary according to where they have the procedure.
Silicon Valley-based digital health company Eko announced Eko Home, a new service that enables precise remote monitoring of cardiac function using electrocardiogram (ECG) and heart sounds. Eko Home can be used to create drug-data combinations to demonstrate real-world efficacy for pharma trials, while simultaneously allowing clinicians to collect high-quality data while outside of the clinical environment.
Nate Bachman, graduate research assistant in the Human Cardiovascular Physiology Lab of the Dept. of Health and Exercise ...
Cardiac positron emission tomography (PET) is growing in popularity among cardiologists because it provides the ability ...
Procyrion Inc. secured Breakthrough Device designation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its Aortix System. Aortix is a circulatory support device for chronic heart failure patients on medical management who have been hospitalized for acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) with worsening renal function.
High blood pressure among children is on the rise and a lack of research about how to treat it has left pediatricians trying to make their best guess. That’s until researchers at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) released results of a pioneering study that used a series of personalized trials to identify a preferred therapy for kids – the first step in tackling the problem.
Cancer patients taking cholesterol-lowering statin medication following radiation therapy of the chest, neck or head had significantly reduced risk of suffering a stroke, and possibly other cardiovascular complications, according to new research. The research appeared in Journal of the American Heart Association.
When performing radiofrequency (RF) ablation to treat cardiac arrhythmia, medical professionals must balance the safety ...
The loss of a single gene two to three million years ago in our ancestors may have resulted in a heightened risk of cardiovascular disease in all humans as a species, according to new research. Loss of the gene may have also set up a further risk for red meat-eating humans. The findings were published July 22, 2019 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Significantly more patients suffer cardiac arrests in U.S. hospitals each year than previously estimated, according to new research in Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes, an American Heart Association journal.
Mark Ibrahim, M.D., FACC, assistant professor of medicine and radiology, associate program director, advanced cardiac ...
Change Healthcare Cardiology Hemodynamics is an integrated hemodynamic monitoring system for monitoring vital signs and ...
Andrew Choi, M.D., FACC, FSCCT, co-director, cardiac CT and MRI, assistant professor of medicine and radiology, George ...
A highly competitive $4.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) will support Keck School of Medicine of USC efforts to recruit patients from underrepresented populations into cardiac surgery clinical trials. The seven-year grant funds the Keck School’s ongoing research contributions to the Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network (CTSN), the formal NIH infrastructure for conducting major clinical trials in cardiac surgery. The grant also establishes an implementation science training program to address the critical need to develop methods to translate clinical research findings into clinical practice.
A new article published in AACN Advanced Critical Care outlines the traditional anticoagulant therapies familiar to most critical care providers as well as newer medications introduced in recent years. “Anticoagulant Medications for the Prevention and Treatment of Thromboembolism” will help nurses and other advanced practice providers to stay current on the latest research and evidence-based practice related to patients with hematologic and oncologic disorders, as these specialties continually evolve.


 August 01, 2019
August 01, 2019