The first randomized trial to compare a durable polymer drug- eluting stent to a polymer-free drug-coated stent in patients at high risk of bleeding and treated with one-month dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) found that both are clinically safe and effective.
A biodegradable polymer everolimus-eluting stent (BP-EES) followed by four months of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) is safe and effective in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for unprotected left main coronary artery (uLMCA) disease. These findings are courtesy of the IDEAL-LM trial, which compared BP-EES plus four months of DAPT to a conventional durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent (DP-EES) followed by 12 months of DAPT.
A discussion with William O’Neill, M.D., director of the Henry Ford structural heart program, Ruth Fisher, MBA, vice ...
Providing exceptional cardiovascular care for patients to achieve the best possible outcomes is the number one goal for ...
Data from the EVOLVE Short DAPT study found that shortened three-month dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) did not increase myocardial infarction (MI) or stent thrombosis (ST) in high bleeding risk (HBR) patients treated with a contemporary drug-eluting stent.
A discussion with Ruth Fisher, MBA, vice president of the Henry Ford Hospital structural heart program, and Janet Wyman ...
A discussion with Nicolas Bevins, Ph.D., vice chair, physics and research, and Jessica Harrington, RCIS. They explain ...
Cardiac positron emission tomography (PET) is growing in popularity among cardiologists because it provides the ability ...
A discussion with Khaldoon Alaswad, M.D., director, cardiac catheterization lab, Henry Ford Hospital, on treating ...
Ancora Heart Inc. announced results from an interim analysis of heart failure patients treated in the CorCinch FMR study, a U.S. early feasibility study. CorCinch FMR evaluated the safety of the investigational AccuCinch Ventricular Repair System designed for the treatment of systolic heart failure. The data was presented at the 31st Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT), the annual scientific symposium of the Cardiovascular Research Foundation, Sept. 24-29 in San Francisco.
Abiomed’s newest heart pump, the Impella 5.5 with SmartAssist, has received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) pre-market approval (PMA) for safety and efficacy in the therapy of cardiogenic shock for up to 14 days.
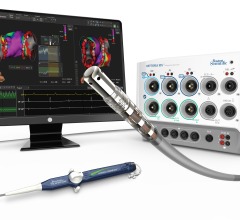
When performing radiofrequency (RF) ablation to treat cardiac arrhythmia, medical professionals must balance the safety ...
EchoPixel introduced what it calls the first-ever intraoperative software to provide naked-eye, touchless interactive 3-D anatomical imaging to support structural heart procedures in the cath lab, operating room (OR) and hybrid OR. The introduction was made at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) 2019 meeting, September 25-29, in San Francisco. The company will showcase the turnkey intraoperative solution, which is pending U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 510(k) clearance, as part of its existing integrated suite of mixed reality software solutions that assist cardiologists and surgeons with visualization of live 3-D medical images during a procedure for more precise catheter and device placement and personalized planning.
Akshay Khandelwal, M.D., director of medical operations at the Henry Ford Heart and Vascular Institute, Detroit, and ...
Clifford Robinson, M.D., associate professor of radiation oncology, chief of the SBRT service, director of clinical ...
Change Healthcare Cardiology Hemodynamics is an integrated hemodynamic monitoring system for monitoring vital signs and ...
New data from the Phase IV independent TWILIGHT trial showed Brilinta (ticagrelor) monotherapy reduced the risk of BARC type 2, 3 or 5 bleeding in high-bleed-risk patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and completed three months of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) at 12 months. Brilinta monotherapy (90 mg twice daily) was compared to Brilinta plus low-dose aspirin.
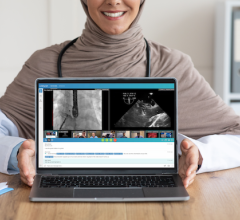
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared three modules of AI-Rad Companion Chest CT, an intelligent software assistant from Siemens Healthineers that brings artificial intelligence (AI) to computed tomography (CT). They include the AI-Rad Companion Engine (K183272), Pulmonary (K183271) and Cardiovascular (K183268) modules. Representing the first intelligent assistant of the new AI-Rad Companion platform, AI-Rad Companion Chest CT helps radiologists interpret images of the thorax (chest) quickly with desired accuracy and precision, and automatically documents these findings as structured reports.
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) analysis can be performed significantly faster with similar precision to experts when using automated machine learning, according to new research. The study was published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging, an American Heart Association journal.


 September 30, 2019
September 30, 2019