Distinguished physicians from leading cardiac surgery centers gathered at an educational symposium to share their experiences with a new-generation blood evacuation system for use following cardiothoracic surgical procedures.
Health Canada granted SunTech Medical a Medical Device License for the Tango M2 Non-Invasive Blood Pressure (NIBP) Monitor

June 18, 2014 — Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories, along with collaborators from Rice University and the Tokyo Institute of Technology, are developing new terahertz detectors based on carbon nanotubes that could lead to significant improvements in medical imaging, airport passenger screening, food inspection and other applications.
Cardiac PET/CT represents a major advancement in cardiovascular diagnostics, offering significant clinical and ...
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for its Edwards Sapien XT transcatheter aortic heart valve for the treatment of high-risk and inoperable patients suffering from severe symptomatic aortic stenosis (AS). This next-generation, lower-profile system, which includes the 29 mm valve size for patients with a large native annulus, will allow for the treatment of more patients. ??
June 17, 2014 — A total of 16 pioneering medical innovations were showcased in front of approximately 4,000 healthcare providers and experts at Premier Inc.'s sixth annual Innovation Celebration, such as the world's first and only intravenous implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD).
June 17, 2014 — AtheroNova Inc. received a Notice of Issuance for an additional compound for cardiovascular treatments. This patent issuance further exemplifies a plan to develop a broad platform of intellectual property involving atheroma stabilization and reduction, lipid modulation and other metabolic diseases.
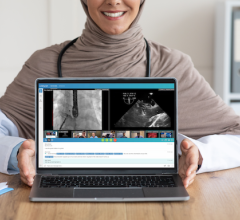
SPONSORED CONTENT — Studycast is a comprehensive imaging workflow system that allows healthcare professionals to work ...
June 17, 2014 — University Hospitals (UH) Case Medical Center is among the first in the country to offer the BioSense Webster's ThermoCool SmartTouch catheter, the first catheter approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to feature direct contact force technology for the treatment of patients with atrial fibrillation.

Interventional thought leaders at an American College of Cardiology (ACC) meeting shared their predictions about the cutting-edge technologies emerging today that will become commonplace in the cath lab of the future.
C. R. Bard Inc. announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) Circulatory System Devices Advisory Panel provided a unanimous favorable recommendation to FDA for use of the Lutonix Drug Coated Balloon PTA Catheter (DCB) in the United States.
Providing exceptional cardiovascular care for patients to achieve the best possible outcomes is the number one goal for ...
New appropriate use expert consensus documents developed by the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) provide guidance on treating the most common form of peripheral artery disease (PAD), namely blockages that affect arteries above the knee.
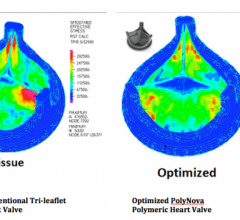
June 16, 2014 — PolyNova, a startup company that has grown out of an inter-institutional collaboration between the University of Arizona (UA) and Stony Brook University, announced it is developing a novel polymeric prosthetic heart valve. Sarver Heart Center cardiologist Marvin J. Slepian, M.D., professor of medicine and biomedical engineering at the UA, is the founding CEO of the new venture. PolyNova entered an exclusive option to the patent rights jointly held by the two universities earlier this spring.
June 16, 2014 — Carestream’s Smart Link helps ensure optimal system performance and uptime by continuously monitoring operations of its healthcare IT and digital imaging systems at healthcare providers across the globe. Smart Link is provided as part of Carestream’s customer service maintenance agreements.
Cardiac positron emission tomography (PET) is growing in popularity among cardiologists because it provides the ability ...
June 16, 2014 — Boston Scientific Corp. has initiated the RESPOND post-market registry to assess real-world performance of the Lotus valve system. The RESPOND registry will collect data on clinical outcomes and device performance in 1,000 patients implanted at 50 centers around the world.

June 16, 2014 — Children with heart disease are exposed to low levels of radiation during X-rays, which do not significantly raise their lifetime cancer risk. However, children who undergo repeated complex imaging tests that deliver higher doses of radiation may have a slightly increased lifetime risk of cancer, according to researchers at Duke Medicine. The findings, published June 9 in the American Heart Association (AHA) journal Circulation, represent the largest study of cumulative radiation doses in children with heart disease and associated predictions of lifetime cancer risk.

Medtronic announced it is purchasing Covidien in a cash-and-stock deal for $42.9 billion. Once the transaction is completed, Medtronic will have significantly advanced its position as a premier international medical technology and services company.


 June 18, 2014
June 18, 2014