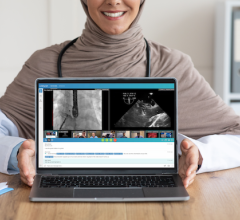
Ziyad Hijazi, M.D., MPH, MSCAI, FACC, director of the cardiac program and chair of the Department of Pediatrics at Sidra ...
Philips announced its presence at the Vascular Interventional Advances (VIVA 17) Annual Conference in Las Vegas from Sept. 11 – 14, 2017, applying advanced technologies and deep clinical insights to address peripheral vascular needs. With the addition of its recent acquisition, Spectranetics, Philips will for the first time highlight its expanded portfolio of interventional X-ray systems, advanced catheters for measurement and therapy, clinical informatics and services, including its Philips Azurion image-guided therapy platform, intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), Phoenix atherectomy system and Spectranetics' Stellarex drug-coated balloon.
Medtronic plc announced that the In.Pact Admiral Drug-Coated Balloon (DCB) received approval from the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) for the treatment of peripheral artery disease (PAD) in the upper leg — specifically, in the superficial femoral arteries (SFA) and popliteal arteries. Before Medtronic can begin commercialization, it must partner with Japanese MHLW to gain reimbursement to ensure broader access to the therapy.
Providing exceptional cardiovascular care for patients to achieve the best possible outcomes is the number one goal for ...
A subset analysis of the DETOUR I clinical trial showed promising safety and effectiveness results of PQ Bypass’ Detour System for treating long-segment (>25 cm) blockages in the femoropopliteal artery. The data were presented as a late-breaking clinical trial session at Vascular InterVentional Advances (VIVA 17), Sept. 11-14 in Las Vegas. DETOUR I trial results were presented by Sean Lyden, M.D., chairman of the department of Vascular Surgery at Cleveland Clinic.
Contracting shingles, a reactivation of the chickenpox virus, increases a person’s risk of stroke and heart attack, according to a research letter published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
September 12, 2017 — A new screening program for vascular disease saves one life for every 169 men assessed, according ...
Cardiac positron emission tomography (PET) is growing in popularity among cardiologists because it provides the ability ...
September 12, 2017 — Inclisiran lowers low-density lipoprotein (LDL, or “bad”) cholesterol for up to one year in ...
September 12, 2017 — Very aggressive reduction of LDL-cholesterol to ultra-low levels was associated with progressively ...
September 12, 2017 — The IL-1β inhibitor canakinumab lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease and lung cancer risk by ...
When performing radiofrequency (RF) ablation to treat cardiac arrhythmia, medical professionals must balance the safety ...
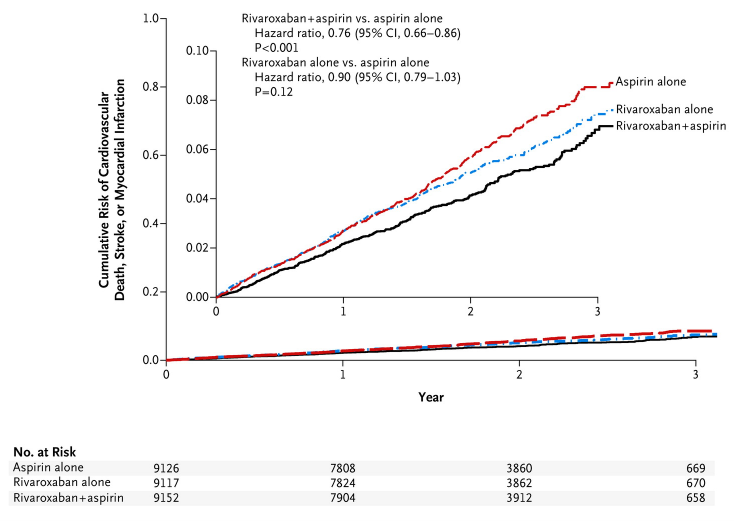
September 12, 2017 — Rivaroxaban plus aspirin improves survival and reduces stroke and heart attack in patients with ...
Hoag Memorial Hospital Presbyterian recently became the first hospital in Orange County, Calif., to install the Siemens Somatom Force computed tomography (CT) scanner. The Somatom Force allows radiologists to obtain higher-quality images faster, more efficiently and with less radiation than older-generation CT scanners.

September 12, 2017 – The Cardiovascular Research Foundation (CRF) announced the promotion of Juan F. Granada, M.D., as ...
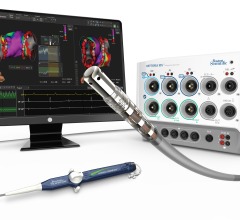
Change Healthcare Cardiology Hemodynamics is an integrated hemodynamic monitoring system for monitoring vital signs and ...
September 12, 2017 – The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2017 includes several Hot Line Late-breaking ...
September 11, 2017 — According to the latest market study released by Technavio, the global electrophysiology ...
Merck and researchers in the Clinical Trial Service Unit at the University of Oxford announced the publication and presentation of results from the REVEAL outcomes study of anacetrapib, Merck’s investigational cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor. In the study of 30,449 patients with atherosclerotic vascular disease receiving LDL-C lowering treatment with atorvastatin, anacetrapib significantly reduced the risk of major coronary events (composite of coronary death, myocardial infarction or coronary revascularization) by 9 percent relative to placebo (10.8% vs. 11.8%, respectively; P=0.004). The safety of anacetrapib was generally consistent with data from earlier trials of the drug. However, a sub-study also showed that anacetrapib accumulates in adipose tissue with prolonged dosing.


 September 13, 2017
September 13, 2017