August 7, 2017 — Virtual Phantoms Inc. announced the release of VirtualDoseIR, a tool for assessing organ dose from interventional radiology (IR) procedures. Like its VirtualDose CT product for computed tomography, VirtualDoseIR combines a family of anatomically realistic human phantoms, advanced Monte Carlo simulations, and an easy-to-use web interface to provide realistic calculations of dose to a diverse patient population.
VirtualDoseIR enables users to accurately compute doses to radiosensitive organs for a broad range of the patient population, including those outside the “average” body size, pediatric patients from newborn through adolescence, and patients who are pregnant.
In recent years, IR procedures have expanded beyond the traditional cardiovascular applications to many other specialty areas, and so their overall use has increased significantly, today contributing more than 14 percent of all medical radiation dose in the United States. Long exposure times can subject patients to acute injuries to the skin and other tissues, but the large accumulated doses pose a long-term radiation risk that can be monitored and managed. With continued growth, it is likely that regulatory attention will turn to IR in the future.
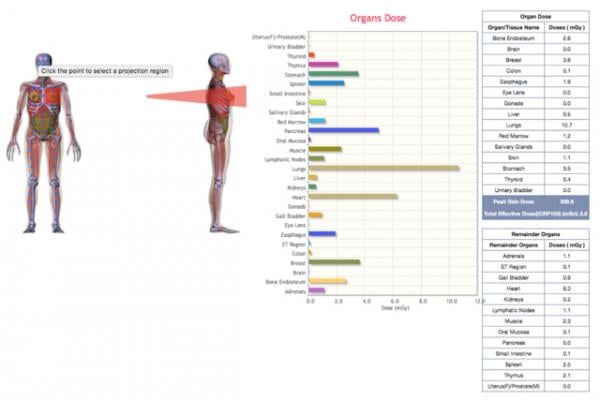
VirtualDoseIR has been designed with clinical practice in mind. The web interface allows the user to easily select the parameters of the procedure setup, including field size, kVp, filtration, position and direction. As these are selected, the display updates to provide a visualization of the exam field on the patient to ensure it matches the procedure performed. And because different machines may track different information, the system will accept X-ray output in terms of dose area product (DAP) or air kerma rate and exposure time.
For more information: www.virtualphantoms.com


 November 13, 2025
November 13, 2025