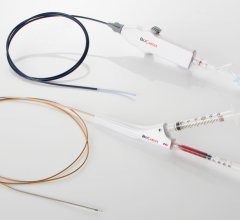
January 19, 2015 — The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted a humanitarian device exemption for the CVRx Inc. Barostim neo Legacy System.
The Barostim neo System is a programmable, minimally invasive device that consists of an implantable pulse generator (IPG), a 2-mm electrode and an external programmer. Barostim therapy is designed to trigger the natural blood pressure regulation system by electrically activating the carotid baroreceptors. The device is commercially available in Europe and the United States. The therapy is included in the joint European Society of Hypertension and European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the treatment of resistant hypertension published in June 2013.
The system is completed by connecting the IPG to electrical stimulation lead electrodes placed on the carotid sinus nerves on each side of the neck. The device provides controlled delivery of high-frequency, small electrical stimulation pulses to the carotid sinus. This has been shown to provide probable benefit to patients with resistant hypertension who have already been determined to respond to this treatment by lowering their systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
The Barostim neo Legacy System may be used in patients with resistant hypertension who were previously implanted in clinical trials with the Rheos Carotid Sinus Leads Models 1010R, 1010L, 1014L, and 1014R which have now been discontinued and are no longer available. Specifically, the approved IPG will replace an existing IPG in a patient whose battery is depleted and needs to be replaced and/or electrode lead repair procedures are necessary.
Use of the Barostim neo Legacy System may help patients who achieved a significant lowering of their blood pressure during their participation in the clinical trial to maintain those results. Clinical trial results showed that in these patients the systolic and diastolic blood pressure was lowered by an average of 33.6 mmHg and 17.5 mmHg, respectively.
For more information: www.fda.gov


 January 29, 2026
January 29, 2026