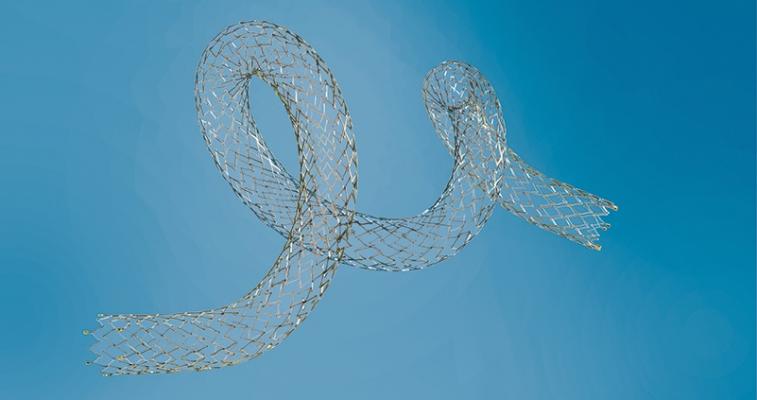
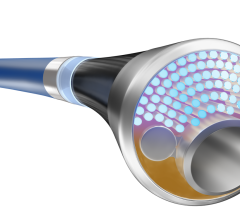
December 13, 2016 — Biotronik announced the presentation of data confirming the efficacy of the Pulsar-18 bare metal self-expanding stent (BMS SE) at VEITHsymposium 2016, Nov. 15-19 in New York. Jos C. van den Berg, University of Bern, Switzerland, presented the encouraging interim results for Pulsar-18 in treatment of superficial femoral artery (SFA) disease during the symposium’s main program on behalf of lead investigator for the BIOFLEX PEACE all-comers trial, Michael Lichtenberg, Vascular Center, Arnsberg, Germany.
BIOFLEX PEACE is a prospective, multi-center registry examining 151 all-comers; the primary endpoint is primary patency at 12 months. The available 12-month interim results demonstrate that Pulsar-18 is an effective treatment option in the SFA. The primary patency rate of 75 percent and freedom from target lesion revascularization (TLR) of 93.1 percent confirm the results of previous Pulsar studies.1,2 Clinical success of 85 percent (defined as improvement in Rutherford class ≥1) has also been observed.
“It is reassuring to see that the clinical outcomes in this real world registry are similar to already published 12-month data,” stated van den Berg. “These positive results were obtained with the Pulsar stent, which has a thin strut design producing a low chronic outward force (COF). As higher COF has been shown to result in higher restenosis rates3, Pulsar’s unique design can be combined with minimal oversizing to further reduce COF for better outcomes.
Pulsar stents are manufactured with Biotronik’s proBIO coating, a silicon carbide layer that reduces metal ion release from the stent surface into the surrounding tissue. Pulsar-18 is available in diameters of 4 to 7 mm, all deliverable through a 4 F sheath.
The Pulsar-18 stent is an investigational device limited by United States law to investigational use.
For more information: www.biotronik.com
References:
1. Bosiers M et al. J Endovasc Ther. 2013, 20(6).
2. Lichtenberg M et al. J Endovasc Ther. 2014, 21(3).
3. Zhao H et al. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009, 32(4).


 September 12, 2025
September 12, 2025