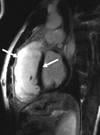
August 18, 2009 - Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) represents a safe, noninvasive modality that frequently helps guide patient management, according to early findings from a multicenter registry published online Aug. 11 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Lead investigator, Oliver Bruder, M.D., of Elisabeth Hospital (Essen, Germany),* and his team looked at how CMR imaging was utilized in 11,040 consecutive patients enrolled in the pilot phase of the EuroCMR (European Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance) registry at 20 participating sites between April 2007 and January 2009. The researchers assessed the indications for CMR as well as its procedural safety, image quality and clinical value in a routine setting.
In the study, 88 percent of patients received a gadolinium-based contrast agent during the imaging procedure, with a median contrast dose of 1.28 mmol/kg (1.16-1.56 mmol/kg) bodyweight. The vast majority of MR procedures were performed without complications. Mild complications, which occurred in 1.1 percent of patients (n=124), were associated with butamine or adenosine infusion during stress testing, and included dyspnea, chest pain and extra systoles. All five severe complications were related to stress testing; there were no deaths. Moreover, the safety of the procedure did not depend on age, gender or race.
The main indications for cardiovascular MR were as a workup for myocarditis and cardiomyopathies (31.9 percent), risk stratification in patients with suspected CAD/ischemia (30.8 percent), and assessment of myocardial viability (14.7 percent).
• Bruder O., Schneider S., Nothnagel D., et al. EuroCMR (European Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance) registry. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2009; E-pub ahead of print.
For more information: content.onlinejacc.org


 January 21, 2026
January 21, 2026