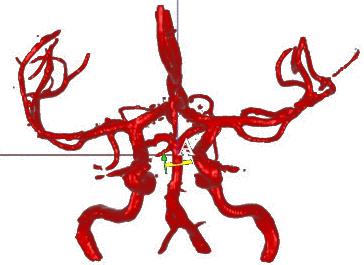
Image courtesy of VasSol Inc.
February 20, 2015 — A recently completed National Institutes of Health-funded trial confirms the efficacy of blood flow measurement technology from VasSol Inc. to predict the possibility of repeated stroke in at-risk individuals.
VasSol’s NOVA (Non-invasive Optimal Vessel Analysis) software provided the quantitative data that underpinned the VERiTAS (Vertebrobasilar Flow Evaluation and Risk of Transient Ischemic Attack and Stroke) clinical trial, which found that low blood flow to the back of the brain increased patients’ risk of recurrent strokes. The results, presented at the International Stroke Conference 2015, are expected to substantially improve both the study and treatment of stroke, the fourth leading cause of death in the United States, and the leading cause of permanent disability among Americans.
The trial observed 80 patients who had recently suffered a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) affecting the blood supply to the back of the brain, known as the vertebrobasilar area. Posterior circulation strokes account for 30-40 percent of all ischemic strokes – approximately 200,000 cases annually in the United States alone.
Over a two-year period, each participant received a baseline and three subsequent quantitative magnetic resonance angiography (qMRA) tests using NOVA software to quantify the volumetric blood flow rate in vessels of the brain. NOVA tests provided researchers with a three-dimensional view of the blood vessel being studied as well as measurements in cubic centimeters per minute of how much blood is flowing, how fast and in what direction.
The results identified approximately one-quarter of those enrolled as having low posterior blood flow. Those individuals had a stroke risk four and one-half times higher during the first 12 months of the study than those participants with normal blood flow. When studied for a full 24 months, those with low blood flow had a stroke rate of 30 percent versus 13 percent for patients with normal blood flow.
“Identifying those at highest risk for a stroke makes studying the condition easier and leads to better, more precise therapies and more focused implementation of healthcare resources,” said Fady Charbel, M.D., inventor of NOVA, which runs on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment found in most hospitals and imaging centers worldwide. Chairman of neurosurgery at the University of Illinois at Chicago Hospital, where much of the product’s research took place, Charbel founded VasSol in 2001 to commercialize NOVA and continues as the company’s chief scientific officer.
“More aggressive procedures such as angioplasty and stenting carry significant risks and are expensive. However, they may be necessary for high-risk patients. NOVA provides information that an MRI alone can’t provide. And because it helps patients receive the appropriate treatment, it improves patient safety and reduces healthcare costs,” he said.
NOVA received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in 2001.
For more information: www.vassolinc.com


 January 05, 2026
January 05, 2026 









