Clinical trial quality data can be derived from national cardiovascular registries, which may change how trials are performed in the future. Getty Images
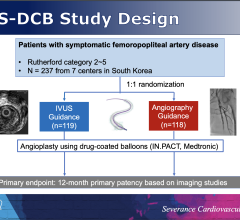
June 24, 2021 — Data captured in American College of Cardiology (ACC) National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) registries is similar in quality, depth and granularity when compared to data captured through clinical trials, according to research in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.[1] The study that compared data from the DAPT Study to NCDR CathPCI Registry data.
This may be good news for streamlining data collection and supports recent efforts to standardize data elements and definitions used in clinical trials and registries. There has been discussion by many cardiology experts the past several years that clinical trial quality data insights can be pulled from the real-world procedural data collected in these registries.
“We found an overall high level of similarity in data between these two sources. This suggests that registries may also be suitable to support baseline data collection for many clinical studies,” said senior study author Robert W. Yeh, M.D., MSc, director of the Richard A. and Susan F. Smith Center for Outcomes Research in Cardiology at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and associate professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. “Being able to leverage existing registries to provide data for clinical trials has the potential to greatly enhance the efficiency and lower the costs of conducting these important studies.”
The researchers linked a group of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy (DAPT) Study patients to the NCDR CathPCI Registry and compared data elements for the same patients. All patients receiving percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stents randomized in the DAPT Study who could be linked to the CathPCI Registry were included. Baseline patient and procedural characteristics were compared using data collected by two methods: reports submitted by DAPT Study investigators and site-reported data submitted to the CathPCI Registry.
Out of 8,864 DAPT Study patients, 5,743 (65%) were successfully matched to data in the CathPCI Registry. There was strong agreement with many data elements, including demographics and procedural characteristics. For some prior history and risk factors, there was more modest agreement and agreement was poor for clinical presentation. According to the researchers, most notably, angina was more likely to be classified as unstable in the CathPCI Registry versus the DAPT Study.
The results suggest that CathPCI Registry data could be used to support future clinical trials, decreasing the burden of data collection on sites participating in both trials and the registry. However, variables that could be considered more subjective, such as clinical presentation, would likely need to be defined more precisely. Future trials leveraging the CathPCI Registry would also need to ensure that the key data elements are suitable to answer key trial questions.
“Whether these findings generalize to other types of data in the CathPCI Registry or other clinical registries is unknown and remains a rich area for future inquiry,” Yeh said. “Overall, however, the data are promising in pointing to an important mechanism to make clinical trials more feasible and less costly, helping to overcome one of the most significant barriers to clinical research.”
The primary limitations of the study were the inability to link all patients. In addition, how these results would have fared for other clinical trials is unknown.
Reference:


 July 31, 2024
July 31, 2024