September 25, 2020 — Short-term hydroxychloroquine treatment is not associated with lethal heart rhythms in patients with COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) who are risk assessed prior to receiving the drug. That is the finding of research published today in EP Europace, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).[1]
“This was the largest study to assess the risk of dangerous heart rhythms (arrhythmias) in COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine,” said study author Dr. Alessio Gasperetti of Monzino Cardiology Centre, Milan, Italy and University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland. “In our cohort, there was a low rate of arrhythmias and none were associated with hydroxychloroquine.”
The study began when there was very little experience using hydroxychloroquine to treat patients with COVID-19. Current evidence suggests that it is ineffective in patients with advanced disease but there is debate around its effectiveness in the early phase.2,3 This study was not designed to test the effectiveness of hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 but rather to examine cardiac safety.
Hydroxychloroquine is known to cause an electrical change in the heart in some patients. It is called QT prolongation because of the pattern on the electrocardiogram (ECG). This electrical pattern is linked with an increased risk of deadly heart rhythms.
Hydroxychloroquine has been used for decades to treat lupus and rheumatoid arthritis and prevent malaria. But the COVID-19 pandemic is the first time the drug has been used in large numbers of acutely ill patients with multiple health conditions and possibly receiving other QT-prolonging drugs. The scale of the pandemic raises the likelihood of inherited heart problems that predispose patients to arrhythmias. In addition, changes in blood electrolytes, which can trigger arrhythmias, can occur in those needing treatment in an intensive care unit (ICU).
This study was conducted to assess ECG changes and arrhythmias in COVID-19 patients treated with hydroxychloroquine in different clinical settings.
A total of 649 COVID-19 patients were enrolled from seven institutions between 10 March and 10 April 2020. The average age was 62 years and 46% were men. A risk calculator was used to assess the likelihood of QT prolongation and decide the treatment setting. All patients had an ECG before starting treatment and at least one follow-up measurement.
In all centers, patients took 200 mg hydroxychloroquine twice a day (i.e. a total of 400 mg per day). More than half of patients (58.6%) took a loading dose on the first day, meaning they received 400 mg twice on that day (i.e. a total of 800 mg).
Hydroxychloroquine was administered early after symptom onset in three different care settings: 126 (19.4%) patients were managed at home, 495 (76.3%) were hospitalized in a medical ward, and 28 (4.3%) patients were treated in ICU. In line with real-world practice, 30% of patients received two QT-prolonging drugs, and 13.6% received three (including hydroxychloroquine).
A significant QT interval prolongation was observed in the overall cohort, but the magnitude of the increase was modest and similar across care settings. The most important determinants of QT prolongation during hydroxychloroquine treatment were fever at admission and baseline QT length.
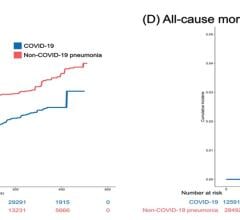
Over a median follow-up of 16 days, there were no lethal arrhythmias. A total of seven patients (1.1%) had a serious ventricular arrhythmia, but none were deemed related to QT prolongation or to hydroxychloroquine treatment.
“Hydroxychloroquine treatment was associated with QT prolongation, as expected, but the change was small," Gasperetti said. "There was no connection between the drug and the occurrence of arrhythmias. The study shows that hydroxychloroquine administration, alone or in combination with other potentially QT-prolonging drugs, is safe for short-term treatment of COVID-19 patients at home or in hospital, provided that they undergo risk assessment and ECG monitoring by a physician.”
Related Content on Cardiac Issues Related to COVID-19 Treatments:
VIDEO: Why QT-prolongation Occurs in COVID-19 Patients on Hydroxychloroquine and Azithromycin — Interview with Andrew D. Krahn, M.D.,
VIDEO: Overview of Hydroxychloroquine and FDA Warning in its use to Treat COVID-19 — Interview with Marianne Pop, Pharm.D.
FDA Revokes Emergency Use Authorization for Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19
COVID-19 Hydroxychloroquine Treatment Brings Prolonged QT Arrhythmia Issues
FDA Reports of Deaths and Injuries From Use of Antimalarial hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 Patients
VIDEO: Cardiologists Manage Trial Testing if Hydroxychloroquine Protects Clinicians From COVID-19 — Interview with William O'Neill, M.D.
First Large-scale U.S. Study on Hydroxychloroquine COVID-19 Prophylaxis Begins in Detroit
COVID-19 Therapy Drug Azithromycin May Increase Risk for Cardiac Events
References:

 March 20, 2024
March 20, 2024