March 19, 2018 — For people at heightened risk for atrial fibrillation (AFib), a common heart rhythm disorder that also carries a high risk of stroke, wearing a self-adhering chest patch that records heart patterns may better detect the condition and facilitate more timely treatment than relying on usual care, according to one-year data presented at the American College of Cardiology’s 67th Annual Scientific Session, March 10-12 in Orlando, Fla.
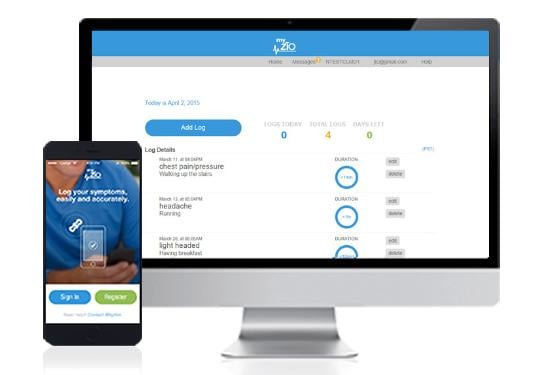
The study, called the mHealth Screening to Prevent Strokes (mSToPS) trial, is one of the first completely digital, nationwide, direct-to-participant and site-less clinical research programs, according to researchers. Patients consented and enrolled exclusively via a web-based platform to undergo active monitoring at home using the iRhythm Zio patch. The patch — about the size of a large Band-Aid — continuously records an electrocardiogram (ECG), the gold standard for detecting AFib. But instead of only providing a brief snapshot of someone’s heart rhythm — which is often the case with an ECG in the clinic — this technology allowed researchers to collect 14 consecutive days of data capturing the electrical activity of an individual’s heart.
“At one year, people who wore the chest monitor had nearly three times the likelihood of being diagnosed with AFib, and appropriately. A significantly higher proportion of these patients were started on anticoagulant therapy to lower their stroke risk compared with those who received usual care,” said Steven R. Steinhubl, M.D., director of digital medicine, Scripps Translational Science Institute, La Jolla, Calif., and lead author of the study. “The data also provide a first glimpse into how this type of ECG screening might influence heart care utilization.”
AFib causes the heart’s upper chambers to beat erratically. In turn, blood can pool in the heart and, if clots form and travel to the brain, can result in a stroke. In fact, people with AFib have a fivefold greater chance of having a stroke than the general population. New estimates suggest that 37 percent of adults over 55 years of age will develop AFib. But Steinhubl said as many as 1 out of 3 patients may be undiagnosed and, therefore, remain susceptible to stroke.
“A stroke is a very devastating cardiovascular complication of AFib; it can be tragic for patients and costly for payers,” Steinhubl said. “If we identify and get these people on a blood thinner, we can reduce their risk of stroke by about 70 percent, which is powerful.”
The mSToPS trial enrolled and monitored a total of 1,732 eligible Aetna patients with no heart rhythm issues but who were at moderate risk for AFib (median CHA2DS2-VASc score of 3) and matched them (2:1) to 3,646 observational controls of similar age, sex and risk profiles who received usual care only; all were included in the analysis. The average patient age was 73.7 years. Once enrolled, participants in the active monitoring group received the wearable chest patch by mail and were given clear written and video instructions on how to use and place the wearable patch. Participants wore it for an average of 12 days and then returned it with a prepaid shipping envelope. The data collected from the patch, currently only U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved for clinical use, are first analyzed with an algorithm that reads the ECG and preliminarily identifies all rhythm abnormalities, including AFib. In the trial analyses, a clinician and a clinical events committee read all potential diagnoses of AFib in a blinded fashion and either agreed or disagreed. All participants received their ECG study report. Researchers also collected and analyzed use of AFib-related medications, doctor and emergency department (ED) visits, and cases of blood clots and stroke.
The primary endpoint was the incidence of AFib at one year. AFib was newly diagnosed in 6.3 percent of those wearing the patch and 2.3 percent of controls. Compared with controls, participants who wore the chest patch had significantly more primary care physician visits (78.7 versus 75 percent,) and cardiology outpatient visits (31.6 versus 23.6 percent), but no difference in ED visits or hospitalizations. Relative to controls, active monitoring with the patch was associated with significantly greater initiation of anticoagulation (5.4 versus 3.4 percent) and small but statistically significant increases in antiarrhythmic therapy (0.8 versus 0.3 percent) and pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator placement (0.7 versus zero percent). Researchers were unable to show that the intervention had an impact on clinical outcomes, including blood clots or stroke, given the short follow-up (eight months on average). Study participants will be followed for another two years to track these events.
Still, Steinhubl said the findings demonstrate a feasible, scalable and clinically valuable way of screening for undiagnosed AFib in an at-risk, nationwide population.
“The quality of data collected through the patch is as good as what we see clinically,” he said. “What was fascinating is that for the people with AFib, the burden of AFib (the amount of time a person was in AFib relative to their entire monitoring time) was quite low — approximately 1 percent of the time on average — a finding that suggests the prevalence of undiagnosed AFib is likely higher than clinicians might suspect, since it can be easy to miss, which could have important implications for how we should ideally screen for the condition.
“In most cases, the only currently recommended method is to feel someone’s pulse or check an ECG for 30 seconds during a routine doctor’s visit,” Steinhubl said. “Based on our data, individuals have very short episodes of AFib that would make it very difficult to catch in the way we routinely look for it today.”
Increasing age is by far the biggest risk factor for AFib, but heart failure, prior stroke and sleep apnea are all additional important risk factors. Steinhubl stressed that one of the most unique and valuable aspects of the study is how it was designed and conducted, including an emphasis on being more participant-centric. Using digital technology, the study was brought directly to the participants, even participants who were 74 years old on average.
“Currently, most people who are able to take part in clinical research live close to academic medical centers,” he said. “In a way, mSToPS is proof of principle that site-less trials are possible and might open up clinical research to anybody, anywhere who is interested in taking part.”
Researchers will continue to follow participants for another two years to assess any differences in reports of strokes or other systemic thromboemboli.
This study was funded, in part, by Janssen Pharmaceuticals; other sponsors include the National Institutes of Health and the Qualcomm Foundation.
For more information on late-breaking news at ACC.18, find links to stories at ACC 2018 Late-Breaking Trials.


 July 31, 2024
July 31, 2024