March 20, 2019 — At the American College of Cardiology’s (ACC) annual meeting, March 16-18 in New Orleans, Philips announced the results of the DEFINE PCI [1] study, which assessed the level of residual ischemia found in patients after percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI). This study found that 1 in 4 patients [1] treated with standard-of-care PCI left the cath lab with residual ischemia (iFR < 0.90), as demonstrated by using a blinded instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR) pullback measurement, which is Philips’ new physiologic guidance technology.
Sponsored by Philips, the DEFINE PCI study involved approximately 500 patients, and was led by investigators from the Cardiovascular Research Foundation, Duke Clinical Research Institute and the Imperial College London.
PCI is an image-guided, minimally invasive treatment to open a coronary artery blockage (stenosis) that is causing a reduced blood flow (ischemia) to the heart tissue. Under interventional X-ray guidance (coronary angiography), clinicians navigate a balloon catheter and coronary stent to the treatment area to deploy them and restore arterial blood flow.
Several studies [2, 3] have revealed that a significant portion of patients treated with coronary stents continue to experience chest pain (angina) following PCI, leading to an increased rate of repeat procedures and corresponding higher costs. The DEFINE PCI study, which took place at centers throughout the U.S. and Europe, shows that the current approach to PCI has limitations for identifying the locations of physiologically significant arterial lesions in patients suffering from coronary artery disease (CAD). Of the patients with residual ischemia, the study showed that 81.6 percent had an untreated focal stenosis (narrowing of an artery). Further analysis of the study data showed that if all focal stenoses had been identified and successfully treated, only 1 in 20 patients would still have residual ischemia. This indicates that if the precise locations causing ischemia are better detected prior to stenting, patient outcomes may be improved.
Watch the VIDEO: iFR Equal to FFR Outcomes in Coronary Lesion Evaluation
Read the article "Easier to Use iFR Equal to Outcomes of FFR in Coronary Lesion Evaluation"
“The findings from the DEFINE PCI study reveal an opportunity for physicians to optimize procedural results and potentially help more people fully benefit from PCI,” said Allen Jeremias, M.D., principal investigator of the DEFINE PCI study.
“The fact that nearly one-quarter of patients had residual ischemia despite an angiographically successful result, mostly due to focal lesions that can easily be treated, has important implications for improving outcomes of patients undergoing stent implantation globally,” said Gregg W. Stone, M.D., professor of medicine at Columbia University Medical Center.
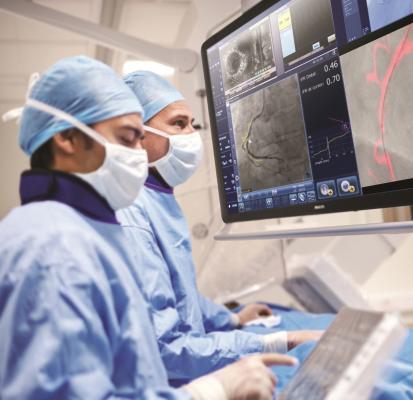
iFR is well-established for determining whether a vessel is indicated for treatment through the landmark DEFINE FLAIR and iFR Swedeheart outcome studies, both published in the New England Journal of Medicine [4, 5]. The one-year patient outcomes were consistent with fractional flow reserve (FFR), while iFR involved less procedural time, reduced patient discomfort and reduced cost [6]. Philips SyncVision iFR Co-registration further advances physiology by mapping the pressure profile of the whole vessel onto the angiogram, providing physiologic guidance for where to treat within the vessel. With iFR Co-registration, physicians can identify the precise locations causing ischemia, plan stent length and placement with a virtual stent, and predict physiologic improvement. Philips SyncVision with iFR Co-registration provides physicians with a full physiologic image allowing them to see clearly and treat optimally.
Read more about late-breaking trials from ACC.19
For more information: www.usa.philips.com/healthcare
References
[1] Jeremias A et al. The DEFINE PCI Trial: Blinded Physiological Assessment of Residual Ischemia after Successful Angiographic Percutaneous Coronary Intervention, presented at ACC 2019.
[2] Recurrent angina after coronary angioplasty: mechanisms, diagnostic and therapeutic options. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3760523/


 July 31, 2024
July 31, 2024