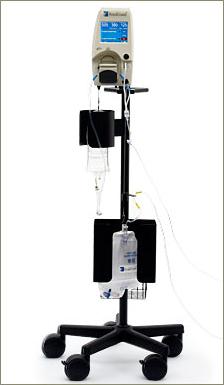
April 3, 2017 — A new meta-analysis further supports the ability of RenalGuard Therapy to significantly reduce the incidence of acute kidney injury associated with cardiovascular interventional procedures compared to other methods of urine volume expansion. Moreover, findings from the analysis show the use of RenalGuard Therapy to be further associated with reduced risk of mortality, major adverse cardiovascular events and the need for post-procedure dialysis.
The research was presented at the 2017 American College of Cardiology (ACC) Annual Scientific Sessions, March 17-19 in Washington, D.C.
A U.S. pivotal clinical trial of RenalGuard is currently on track to complete at the end of 2017, and if positive, RenalGuard Solutions plans to seek U.S. marketing approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2018.
The new meta-analysis, presented as a poster by researchers from the University of Texas Health Sciences Center, San Antonio, included data from nine studies comparing the use of RenalGuard to conventional volume expansion. Six were randomized controlled trials using RenalGuard in the treatment of patients undergoing various cardiovascular diagnostic and therapeutic interventions. Primary outcomes in the analysis included the incidence of contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) and relative risk (RR; the statistical probability that a particular event will occur). Secondary outcomes included the incidence of mortality, major adverse cardiovascular events and the need for post-procedure dialysis.
The investigators found RenalGuard therapy to be associated with a significant risk reduction in CI-AKI compared to the control therapy (RR: 0.409; 95% CI: 0.282-0.591; p<0.001). The incidence of CI-AKI in RenalGuard-treated patients was 8.7% versus 23% in the control group (p < 0.001). Use of RenalGuard was also associated with decreased mortality (RR 0.425, 95% CI: 0.183- 0.987, p = 0.047), dialysis (RR 0.197; 95% CI 0.063-0.614, p=0.005) and MACCE (RR 0.421, 95% CI: 0.273-0.651, p < 0.001) compared to standard hydration.
For more information: www.renalguard.com


 July 31, 2024
July 31, 2024