March 29, 2012 — Adding vorapaxar, an investigational platelet blocker, to standard antiplatelet therapy significantly reduces the risk of recurrent cardiovascular events in a specific group of patients, but also increased the risk of severe bleeding, including intracranial bleeding. This was according to research in the TRA 2°P-TIMI 50 Trial presented during the American College of Cardiology (ACC) 61st Annual Scientific Session in Chicago.
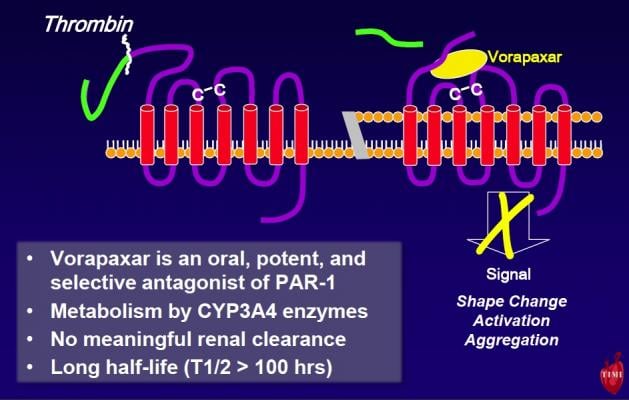
Vorapaxar is the first of a new class of investigational protease activated receptor 1 (PAR-1) thrombin receptor antagonists. Unlike other antithrombotic drugs, vorapaxar blocks thrombin from stimulating platelets to stick together and create clots. Blood thinners, like coumadin, and other antiplatelets like aspirin or clopidogrel, do not directly target these same actions of thrombin.
“In the lab, we have seen very compelling science showing the importance of thrombin’s action on platelets causing blood clots in arteries,” said David A. Morrow, M.D., M.P.H., senior investigator at the TIMI Study Group, director of the Samuel A. Levine Cardiac Unit at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and the study’s lead investigator. “This is the first study to show definitively that blocking this pathway reduces the risk of suffering another cardiovascular event.”
Morrow commented that if vorapaxar becomes available for clinical use, it does not appear suitable for everyone with atherosclerosis. “Of the groups we studied, the benefit was compelling to us only in patients with a prior heart attack,” he said. The new therapy was also found to increase the risk of severe bleeding, including intracranial bleeding. The risk of intracranial bleeding was highest among patients who have suffered from previous strokes; vorapaxar would likely not be appropriate for stroke victims or patients at high risk of bleeding. Stroke patients who were enrolled in the study ended their participation early after advice by the study’s data and safety monitoring board.
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multinational study followed 26,449 patients for more than two years while receiving standard antiplatelet therapy for established atherosclerosis, including previous heart attack (n=17,779), stroke (n=4,883), or atherosclerotic narrowing in the arteries of the legs (n=3,787). Participants were randomly assigned to either take the investigational platelet blocker (2.5 mg orally once daily) with standard therapy, or a placebo with standard therapy.
“It’s exciting to find clearly that we can reduce the risk of a recurrent thrombotic event by adding another platelet inhibitor to aspirin over the long-term,” Morrow said. “Adding this new class of antiplatelet therapy reduced the risk of new cardiac events in stable patients, especially among the subset of patients with a prior heart attack.”
However, he warned patients who took vorapaxar had significantly more bleeding events (GUSTO moderate or severe bleeding at three years 4.2 percent with vorapaxar vs. 2.5 percent with placebo, p<0.001). Intracranial hemorrhage was higher with vorapaxar than placebo (1.0 vs. 0.5 percent, p<0.001) with lower overall rates in patients with no history of stroke (three years: 0.6 percent with vorapaxar vs. 0.4 percent with placebo, p=0.049).
The study was funded by Merck Research Laboratories and was simultaneously published in New England Journal of Medicine and online at the time of presentation at ACC.




 January 28, 2026
January 28, 2026