July 15, 2024 — HeartBeam, Inc., a medical technology company focused on transforming cardiac care through the power of personalized insights, today announced new study data demonstrating that HeartBeam AI combined with vectorcardiography (VCG) outperformed an expert panel of heart rhythm cardiologists in detecting atrial flutter. HeartBeam AI is the company’s deep learning (a form of AI) algorithm for detecting abnormalities in the timing or pattern of heartbeats. The data was presented by Joshua M. Lampert, MD, Cardiac Electrophysiologist, Assistant Professor of Medicine, and Medical Director of Machine Learning for Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, during the Heart Rhythm Society annual meeting in Boston.
In the study, HeartBeam AI was applied to a set of 173 VCGs, single-lead ECGs and 12-lead ECGs to identify atrial flutter. The same set of single-lead ECGs and 12-lead ECGs was reviewed by a panel of three electrophysiologists (EP panel) for atrial flutter, a common arrhythmia that significantly increases a patient’s risk for stroke. Key findings from the analysis show that HeartBeam AI combined with VCG:
- Outperformed an expert panel reviewing single-lead ECGs, with a statistically significant 40% improvement in the detection of atrial flutter cases (sensitivity: 97.3% for HeartBeam AI+VCG vs. 69.4% for EP panel).
- Demonstrated a statistically significant 6% improvement in the detection of atrial flutter cases compared to an expert panel reviewing 12-lead ECGs (sensitivity: 97.3% for HeartBeam AI+VCG vs. 91.1% for EP panel).
- Delivered zero variability in the detection of atrial flutter compared to the EP panel.
Additional details about the study can be found here.
Dr. Lampert commented, “The modern vectorcardiogram is nearly 100 years old, and yet we are cautiously breathing new life into it with the advent of novel acquisition technologies and deep learning algorithms. This study demonstrates that a deep learning algorithm applied to a transformed VCG performs comparably as well when applied to the gold-standard 12-lead ECG. The AI algorithm overall outperformed a panel of electrophysiologists in distinguishing atrial flutter from sinus rhythm with perfect agreement between multiple model predictions compared to significant interobserver variability amongst electrophysiologists, a finding particularly notable on single lead ECG analysis.”
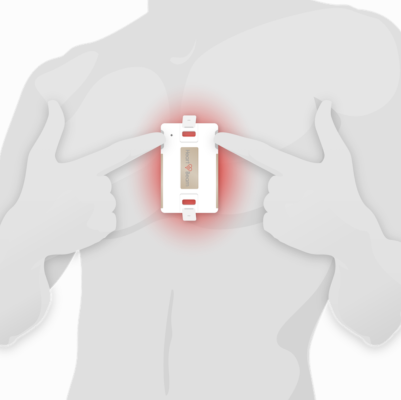
HeartBeam’s core vectorelectrocardiography (3D VECG) technology captures the heart’s signals in three projections (X, Y, Z), similar to VCG, and synthesizes a 12-lead ECG. The Company’s first planned application of the 3D VECG platform technology is HeartBeam AIMIGo™, a credit card-sized device for patient use at home or anywhere, which is currently under review with FDA.
By leveraging AI to analyze the data-rich signals, HeartBeam believes it will be able to improve diagnostic accuracy and to unlock a more personalized approach to cardiac care for patients. As a patient uses AIMIGo over time, there will be a series of ECG readings. HeartBeam aims to leverage AI to analyze the data to provide a longitudinal view of the patient’s cardiac status and move beyond today’s 12-lead ECGs, which typically only provide a snapshot in time.
“The data is incredibly encouraging, showcasing the potential of our artificial intelligence program to improve diagnostic accuracy when a patient is outside of a medical facility,” said Branislav Vajdic, PhD, CEO and Founder of HeartBeam. “We’ll continue to build upon this strong foundation as we advance our AI program to revolutionize cardiac care management in the future.”
Dr. Lampert has no relevant conflicts of interest and HeartBeam did not fund his participation in this work or make the decision to submit the analysis for presentation.
For more information: www.heartbeam.com


 July 30, 2024
July 30, 2024