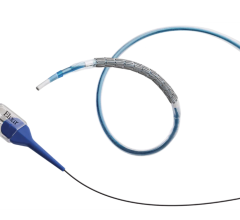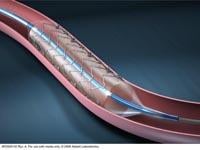
Sept. 14, 2009 – Abbott said today the Chinese State Food and Drug Administration (SFDA) has approved the XIENCE V Everolimus-Eluting Coronary Stent System for the treatment of coronary artery disease (CAD) – the leading cause of death in China.
The company plans a fourth-quarter launch for XIENCE V in China, which is the second-largest drug eluting stent (DES) market in the Asia-Pacific region after Japan. With approval in China, XIENCE V is now available in every Asia-Pacific market except Japan, where approval is anticipated at the end of this year.
According to the China Chronic Heart Disease 2006 Annual Report, nearly 50 percent of all deaths annually in China are due to CAD, and the prevalence of coronary artery disease has steadily increased each year. Approximately 150,000 patients annually undergo a stent procedure for the treatment of CAD, and the number of procedures is growing by more than 20 percent each year in China.
"Heart disease is a serious health issue in China, with more patients being diagnosed each day, so it is critical to have access to advanced technology, such as XIENCE V, that can help improve patient outcomes," said Run Lin Gao, M.D., vice president, Chinese Medical Doctor Association.
"Clinical trial results show that XIENCE V has a strong safety and efficacy profile, with impressively low rates of major adverse cardiac events and target vessel failure. Based on the strength of the data supporting it, XIENCE V is a welcome addition to the heart disease treatment options available to physicians in China," said Yong Huo, M.D., president-elect, Chinese Society of Cardiology.
The XIENCE V drug coated stent will be available in China on the rapid exchange (RX) delivery system. Rapid exchange is the most widely used type of delivery system because it provides physicians additional flexibility to work as single operators during stent procedures.
Abbott's market-leading XIENCE V drug eluting stent is marketed in the United States, Europe and other international markets. XIENCE V is an investigational device in Japan and is currently under review by Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency.
For more in formation: www.xience.cn, www.abbott.com


 July 02, 2024
July 02, 2024