During the annual American College of Cardiology (ACC) scientific sessions, the world’s largest cardiology show, vendors unveil many new technologies. This is a roundup of some of the most innovative new technologies showcased at ACC 2013, including products in the areas of interventional cardiology, patient monitoring, electrophysiology and echocardiography.
iPhone Heart Monitor Hits the Market
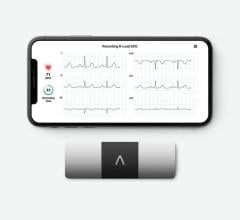
The AliveCor booth was packed all three days with cardiologists who wanted to see a new iPhone-based heart monitor that can be used for patient home monitoring and event monitoring. It is a clinical grade electrocardiogram (ECG) on the iPhone4 and 4S that enables patients to record their heart rhythm anytime, anywhere. The AliveCor Heart Monitor snaps onto the back of an iPhone, like a case, to record, display, store and transfer single-channel ECG rhythms wirelessly with the corresponding, free AliveECG app. Recorded rhythm strips can be of any duration, and are stored in the app and securely in the cloud in PDF format for review, analysis and printing through AliveCor’s HIPAA-compliant website.
The patient places their fingers on the sensors on the rear of the device; there are no leads to attach or special preparation needed. ECG readings are instantly displayed on the iPhone screen.
The heart monitor received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance in November 2012 and was released in the U.S. market in January 2013. The Heart Monitor is available for purchase by medical professionals and by prescription for $199.
Ultrasound Activation Imaging for Better CRT Optimization
A major challenge with cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is finding the optimal location to place leads so the therapy can benefit patients. Toshiba America Medical System unveiled its new activation imaging feature of its 3-D wall motion tracking software. Activation Imaging is an FDA-cleared, proprietary technology available on the Aplio Artida cardiovascular ultrasound system.
When the heart is not functioning properly, different segments activate at different moments in time. Activation Imaging, in conjunction with Toshiba’s wall motion tracking software, allows clinicians to evaluate dyssynchrony at the onset of the heart’s contraction. It also enables proper identification of the left ventricle’s pumping strength and timing for more accurate CRT lead placements.
It displays a color-coded map of the left ventricle to show where a contraction begins, based on the beginning of wall motion. Different colors identify early and late activation. This color-coded map is placed on a 3-D model of the ventricle while the heart is in motion and can easily show normal heart rhythm and abnormalities, such as activation defects due to myocardial infarcts and left bundle branch block.
“Studies show that CRT procedures have a 33 percent failure rate,” said Tomohiro Hasegawa, director, ultrasound business unit, Toshiba. “Activation Imaging’s ability to measure dyssynchrony at a more appropriate moment in time, the onset of contraction, will provide greater confidence during CRT planning to improve patient outcomes and lower healthcare costs.”
Monitoring Dose in the Cath Lab
Toshiba and GE Healthcare both showed new software for their angiography systems that help monitor the level of accumulated skin radiation dose for patients undergoing interventional procedures in the cath lab.
GE’s DoseMap is available on the Innova IGS 5x0 platform. The operator can set predetermined dose thresholds, which when reached, automatically pop up an alert on the overhead screen and queries the physician if they want to change angulation or continue the procedure. The system considers variables in patients that impacts dose absorption, including body mass index, weight, height and the type of intervention.
DoseMap allows the operator to display local cumulative patient dose levels all along the examination and offers the operator the chance to change the dose setting and/or gantry angulation when reaching given thresholds of a procedure. The expected benefit is to help the operator avoid potentially exceeding the local dose threshold and help clinicians better monitor and in turn increase patient care by empowering clinicians to reduce/amend dose levels.
Toshiba demonstrated its recently FDA-cleared dose tracking software for its Infinix-i angiography system. It can be displayed on a screen in the cath lab to show the approximate radiation dose that has been delivered cumulatively to specific areas of a patient. It takes into consideration the amount of time, power setting used and orientation of the C-arm to show a color-coded map of radiation delivery projected on a human figure. The colors change in real time as X-ray imaging continues. It is designed to be a visual reminder to physicians about the dose the patient has received and that they may want to change the location of the C-arm to prevent skin burns during long procedures.
The idea is the same with both vendors' systems, but the Toshiba software visually is easier to understand because it uses a color-coded system instead of using grayscale. The Toshiba system also displays the dose map on a human figure instead of a square box format, so it is easier to interpret.
Radiation Protection With 50 Percent Less Weight
Cath lab radiation protective garment maker Bloxr displayed a new line of aprons, surgical caps and thyroid collars in the GE Healthcare booth that are 50 percent lighter than traditional garments made of lead. The company uses a proprietary polymer material composed of barium and bismuth that makes it very light and flexible. The polymer also allows the garments to be machine washed, unlike lead aprons.
The thyroid protectors and hats are designed to be semi-disposable, where they can be worn for several months and then thrown away. The technology these garments offer addresses infection control issues, where traditional hats and thyroid protectors often become very dirty because of years of use and the build up of dirt and body oils.
Lower Dose Angiography Systems
The FDA cleared Siemens Healthcare’s new Artis Q and Artis Q.zen angiography system families just prior to ACC. The systems feature new X-ray tube and detector technology designed to improve image quality and lower radiation dose. Instead of using coiled filaments from conventional X-ray tubes, Siemens uses new flat emitter technology in the X-ray tube. This enables smaller quadratic focal spots that lead to improved visibility of small vessels up to 70 percent better than conventional X-ray tube technology.
The Artis Q.zen combines this X-ray source with a new detector technology that allows ultra-low-dose ranges as low as half the standard levels applied in angiography. This improvement is the result of several innovations, including a fundamental change in detector design from amorphous silicon to a more homogenous crystalline silicon structure. This structure allows for more effective signal amplification, greatly reducing electronic noise even at ultra-low radiation doses.
IVUS-Angiography Image Integration
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) offers insights on lesions in the coronary arteries, but for vessel segments with several lesions or long diffuse lesions, it is often difficult to correlate where exactly the IVUS catheter imaging tip is in the vessel. In addition to hardware innovations, the Siemens Artis Q and Artis Q.zen systems possess software applications designed to improve interventional imaging. Siemens new IVUS Map software enables the operator to mark the start and end of a vessel being imaged and note the tip of the IVUS catheter. When the pullback begins, the system records the location of catheter tip in relation to a frozen angiographic image of the vessel segment. During IVUS playback, a moving marker shows the location of the IVUS imaging.
Integrating Technologies for the Cath Lab of Tomorrow
Philips Healthcare displayed a cath lab installation seamlessly integrating several futuristic technologies. These include the Corindus CorPath coronary interventional robotic navigation system, Infraredx’s true vessel characterization (TVC) IVUS/infrared spectroscopy intravascular imaging system and Philips’ new 3-D transesophageal echo (TEE) and angiography fusion imaging system.
Philips Healthcare owns a minority share of Corindus Vascular Robotics, which gained FDA clearance last year as the world’s first robotic-assisted system for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The two companies announced a distribution agreement for Corindus’ CorPath 200 System last summer. Philips displayed how the Corindus system integrates into the Allura Xper angiography system cath lab installations. The display included the robotic catheter control unit mounted to the patient table and the lead-lined controller’s cockpit that is set up away from the patient and outside the radiation field.
A new partnership between Philips and Infraredx ensures compatibility between the two systems and allows clinicians to quickly and easily connect the TVC Imaging System to the Allura Xper system. The TVC’s combined IVUS and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) technology enables visualization of lipid core plaques (LCPs – the so-called vulnerable plaques) in the coronary arteries. These plaques are believed to be the cause of heart attack-causing clots when they rupture. They also are widely considered to be responsible for a significant number of stenting procedure complications. If enough clinical evidence can be compiled showing a clear relation between LCPs and heart attacks, the TVC system may play a role in pre-emptive interventions before a heart attack develops, or to identify lesions that are likely to cause complications using conventional PCI techniques.
Receiving FDA approval in March, the Philips’ EchoNavigator software integrates the live views of angiographic X-ray and 3-D TEE ultrasound images. The system shows the orientation of the TEE view on the angiographic image. The user also can place landmark dots on the anatomy in the 3-D echo and it will appear on the angiographic image. As the position of the C-arm is changed, the dots and TEE view guide will rotate along with it to show the TEE orientation.
EchoNavigator was developed in response to an upward trend in the use of minimally invasive cath lab-based interventional procedures that require both angiography and 3-D TEE guidance. Most of these procedures are for the rapidly growing segment of structural heart disease procedures.









 November 21, 2023
November 21, 2023